REST is a WebClient feature which helps the user to invoke a method and retrieve
the results through execution by passing the URL and receiving the response in
different forms. (The activity helps to carry out the following operations: GET,
POST, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, OPTIONS, CONNECT, TRACE).
When does the user need to automate with REST?
The main purpose of using REST in our automation is to perform actions such as
retrieving data, updating information, uploading data, and performing specific tasks
on websites or APIs. There are different methods used to perform different tasks.
For EG., “GET” method is used to fetch the data from the respective web service or
API. “POST, PUT, and PATCH” can be used to update, create, and post data to the
webservice or API. Meanwhile, to delete the data, the "DELETE" method can be used.
These operations can be performed using a service request made in JSON, XML,
PLAIN TEXT, or URLENCODED.
Benefits of REST
1. It is also possible to authenticate or authorize users using REST activity. This can be
performed by providing login credentials or an access token in the request header to
authenticate the resources that are protected.
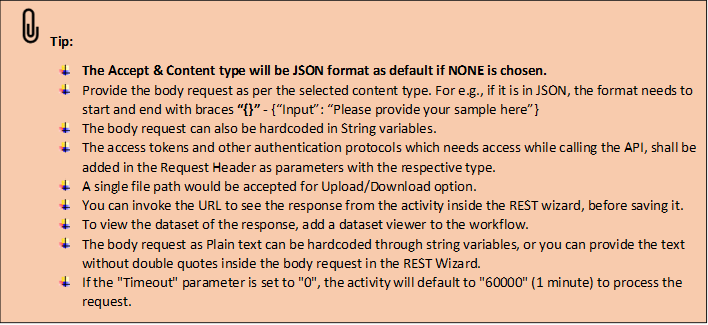
2. File Upload/Download option – The REST activity simplifies the process by enabling
users to upload the request body in file format to the webservice or API in the respective
content type. Alternatively, the users can download the response from the respective file path.
3. REST activity can be used to integrate with external resources or APIs to exchange data
seamlessly.
4. Handle errors and exceptions based on the response code (404, Connection timeout error)
received from the API or webservice.
5. Activities like Amazon S3, Azure Blob, Interact, cognitive services and Robility AI
models available on the Robility Manager can be performed through REST. And other
activities that require cloud storage, messaging services, machine learning services
can be leveraged through API.
Technical Reference
|
|
INPUT |
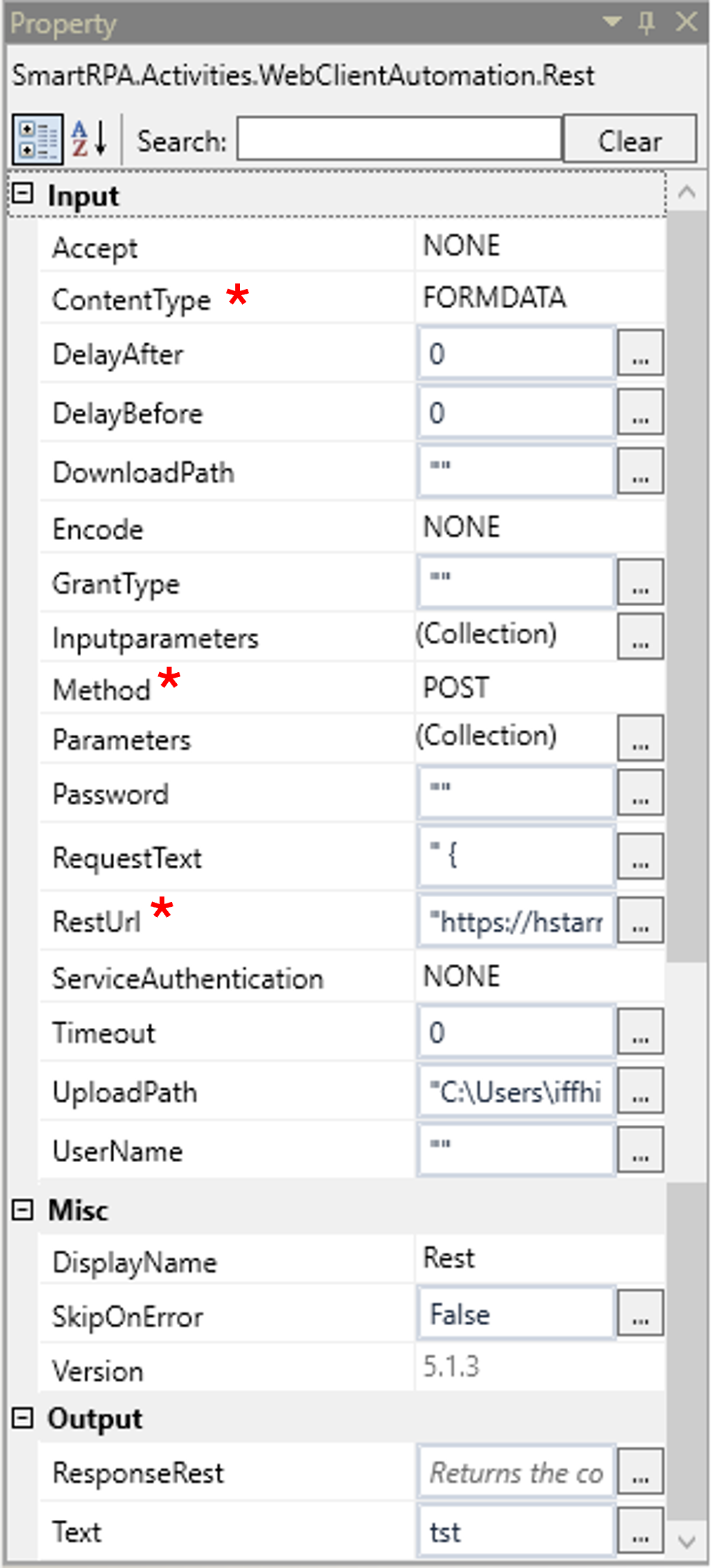
Accept: This specifies the type / format of the web method to accept while processing the URL. Select the options from the drop-down, · None · JSON · XML · URLENCODED · PLAINTEXT · Form-Data This field gets auto filled from Rest wizard after saving it. This is not a mandatory field. By default, it is filled in with JSON. |
|
ContentType: This specifies the type/format of the body request provided. Select the options from the drop-down, · None · JSON · XML · URLENCODED · PLAINTEXT · Form-Data This is a mandatory field. By default, it is filled in with JSON. |
||
|
DelayAfter: It assists the user to add a delay after initiating subsequent activities. The delay duration here is in milliseconds. By default, it is set to zero milliseconds. When the option is left blank, the delay will not be considered. |
||
|
DelayBefore: It assists the user to add a delay before initiating subsequent activities. The delay duration here is in milliseconds. By default, it is set to zero milliseconds. When the option is left blank, the delay will not be considered. |
||
|
DownloadPath: Mention the path of the file where the resources need to be downloaded after calling the method. This is a not a mandatory field. |
||
|
Encode: This specifies the encode format. Select the options from the drop-down, · NONE, · ASCII · DEFAULT · BigEndianUnicode · Unicode · UTF32 · UTF7 · UTF8. |
||
|
GrantType: This field specifies the grant type/ domain of the URL. This is not a mandatory field |
||
|
InputParameters: This specifies the inputs / parameters that is used to request in the URL. This is not a mandatory field. |
||
|
Method: This specifies the method to be used when calling the API URL . The methods that are available are GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, UPDATE, OPTIONS AND TRACE. This is a mandatory field. |
||
|
Parameters: This specifies the parameters that enables to add a custom header to the URL. |
||
|
Password: This field specifies the password that is used to access the web page/ URL. |
||
|
RequestText: This specifies body request needs to be included in the URL. This field supports strings and string variables, JSON, XML, URLENCODED AND PLAINTEXT. This is a mandatory field. |
||
|
ResTURL: This specifies the URL that is used to communicate and get the service. This is a mandatory field. |
||
|
ServiceAuthentication: This specifies the authentication type of the method. |
||
|
Timeout: This parameter indicates the timeout value for establishing a connection to the provided URL. If the connection cannot be established within this specified time, it will throw an exception. This parameter accepts values in “String” datatype. You can either enter the values hardcoded in “String” format or pass the values as “String” datatype. |
||
|
UploadPath: Mention the path of the file that needs to be uploaded as a resource to the URL. |
||
|
Username: This specifies the username that is used to access the webpage/ URL. |
||
|
MISC |
Display Name: Displays the name of the activity. You can also customize the activity name to help troubleshoot issues faster. This name will be used for logging purposes. |
|
|
SkipOnError: It specifies whether to continue executing the workflow even if it throws an error. This supports only Boolean value “True or False” True: Continues to execute the workflow irrespective of any error thrown. False: Stops the workflow if it throws any error |
||
|
Version: It specifies the version of the Web client automation feature in use. |
||
|
OUTPUT |
ResponseRest: Declare a variable here to get the result as dataset from the response. |
|
|
Text: Declare a variable here to get the output as text from the REST response. This is a mandatory field. |
*Represents mandatory fields to execute the workflow.
Rest Wizard
This wizard appears on the screen once the activity is dragged and dropped
to the workflow.
· URL: Enter the URL or API which needs to be called on to make the
request.
· Methods: The REST API can issue requests to the URL, of which
there are eight types:
1. GET- This requests the webpage to extract the information/
details/ Method from the URL. Click here to know a detailed
explanation.
2. PUT- This request is used to update a method/ service in the
URL.
3. POST - This request is used to create a service/ method in the
URL. Click here to know a detailed explanation.
4. DELETE - This requests to removes the service method in the
URL.
5. PATCH - This request is used to send a patch the service/
method to the URL.
6. OPTIONS- This request is used to get the information about the
permissible and supported HTTP methods that can be used against
the provided URL. Click here to know a detailed explanation
7. CONNECT- This request is used to create a connection with
the requested resources.
8. TRACE- This request is used to debug the servers and provides
the response.
· ContentType: This specifies the type/format of the body request that
needs to be. Select the options from the drop-down,
1. None- When None is selected, by default the type is selected
as JSON.
2. JSON - Specifies the type in JSON, if the request that to be made
is in JSON format, choose this option.
3. XML - Specifies the type in XML, if the request that to be made
is in XML node, choose this option.
4. URLENCODED - Specifies the type in URLENCODED, if the request
that to be made is in URLENCODED format, choose this option.
5. PLAINTEXT - Specifies the type as raw text, if the request that to be
made is in RAW Text, choose this option.
6. Form-Data – This content type is used to send data as multipart form
data, typically used for file uploads or when submitting form data
in a way that mimics a web form submission
· Accept: This specifies the type / format of the web method to accept while
processing the URL. Select the options from the drop-down,
1. None- When None is selected, by default the type is selected
as JSON.
2. JSON- Accepts the type in JSON, if the request that to be made
is accepted in JSON.
3. XML - Accepts the type in XML, if the request that to be made
is accepted in XML.
4. URLENCODED - Accepts the type in URLENCODED, if the request
that to be made is accepted in URLENCODED.
5. PLAINTEXT - Accepts the type in PLAINTEXT, if the request that to
be made is accepted in PLAINTEXT.
6. FormData – This indicates that the server is expected to return a
response formatted as multipart form data. This is commonly used
when the response includes multiple parts of data, such as files
and form fields
· Encoding: This specifies the encode format when the request needs to be
encoded while calling the API. Select the options from the drop-down,
1. NONE,
2. ASCII
3. DEFAULT
4. BigEndianUnicode
5. Unicode
6. UTF32
7. UTF7
8. UTF8.
· Authentication: Specifies the authentication protocol to be used when calling
the API. The following protocols are supported:
1. None- Does not require any credentials to invoke the service.
2. BASIC- Username and password will be required to invoke the
services.
3. Default Credentials- Login credentials will be required to invoke
the services.
4. WINDOWS- Domain, username and password will be required
to invoke the services.
5. TOKEN- Domain, username and password will be required to
invoke the services.
· Request Header: This enables to add a custom header that needs to be included
in the URL segment.
· InputParameters: This specifies the inputs / parameters that is used to request in
the URL.
· Body-Request: Specifies body request needs to be included in the URL. This
field supports strings and string variables, JSON, XML, URLENCODED AND
PLAINTEXT.
· File -Transfer: Specifies the file path that needs to be uploaded/ downloaded
as a resource
from the URL.
· Output: The output will be returned as a response to the respective URL provided.
Response codes
Each operation is followed by a HTTP response code that indicates if the request was
successful or not. Here are some typical response codes:
- 200 OK - Request accepted, response contains result.
- 201 CREATED - Resource has been created.
- 204 NO CONTENT - Request accepted, nothing to return.
- 404 NOT FOUND - No such resource.
- 405 METHOD NOT ALLOWED - Method cannot be performed against the resource.
Here’s an example of the activity is used in the workflow –
In the following example, I am using an open-source API with “POST” method. This API
is used to access an open-source online library and using the “POST” method we are
going to add book details to it
Steps to execute a bot
1. Create a new solution.
2. Drag and drop the “REST” activity from the webclient automation feature.
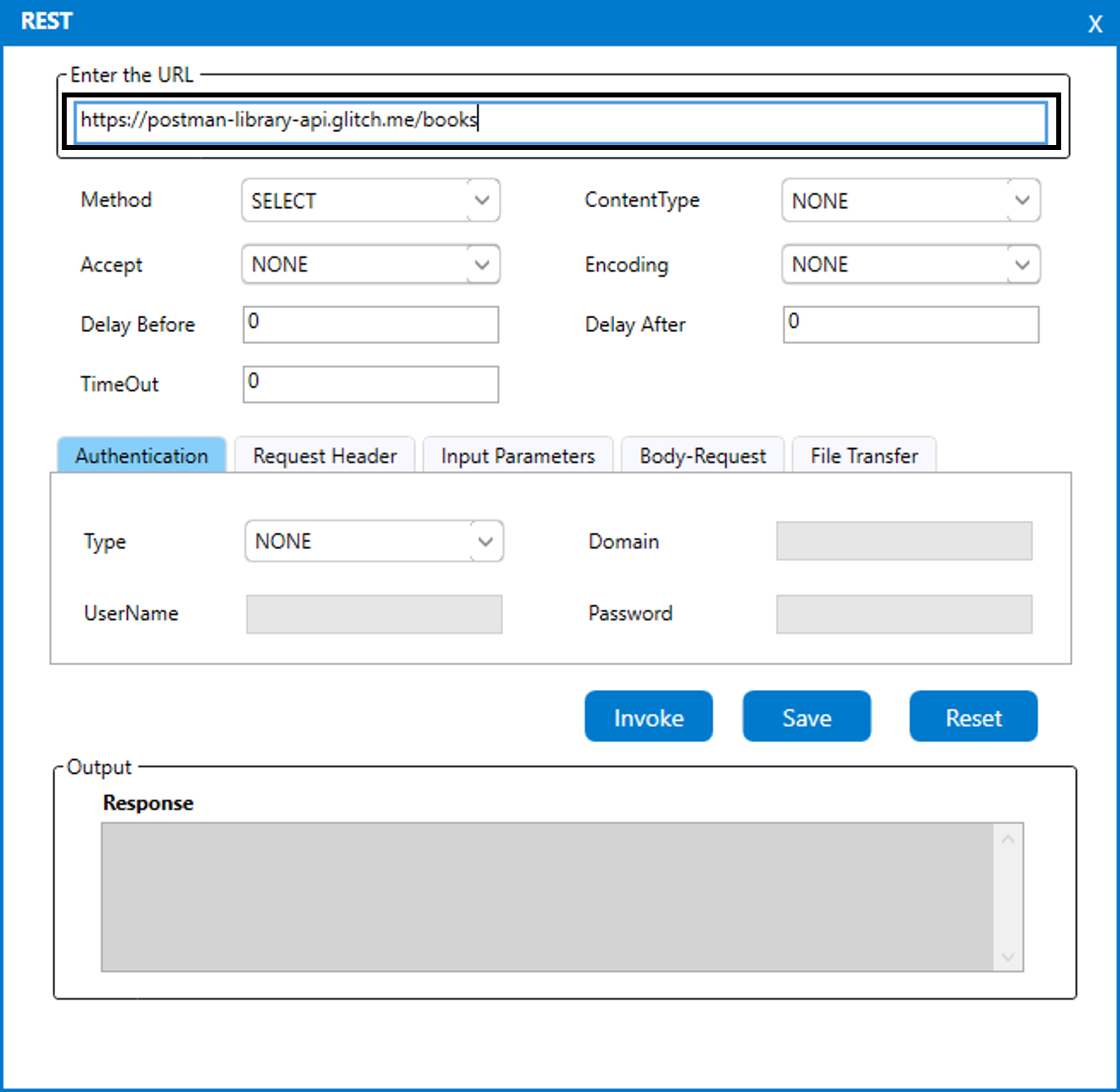
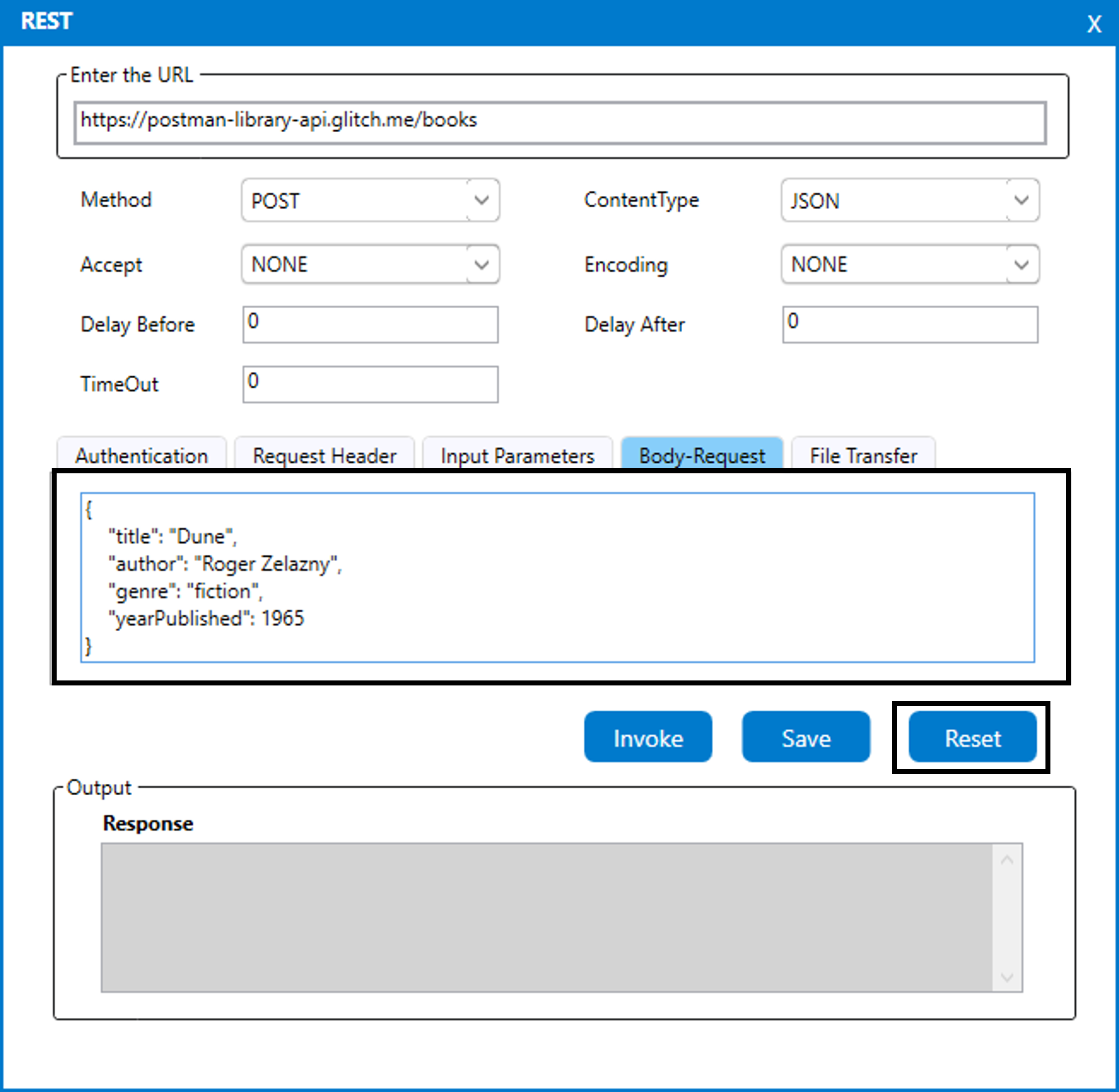
3. The Rest wizard appears on the screen. (Refer the below image).
4. In the “Enter the URL” field, provide the value as “https://postman-library
-api.glitch.me/books."
a. This is the API to access the open-source library. (Refer the below image).
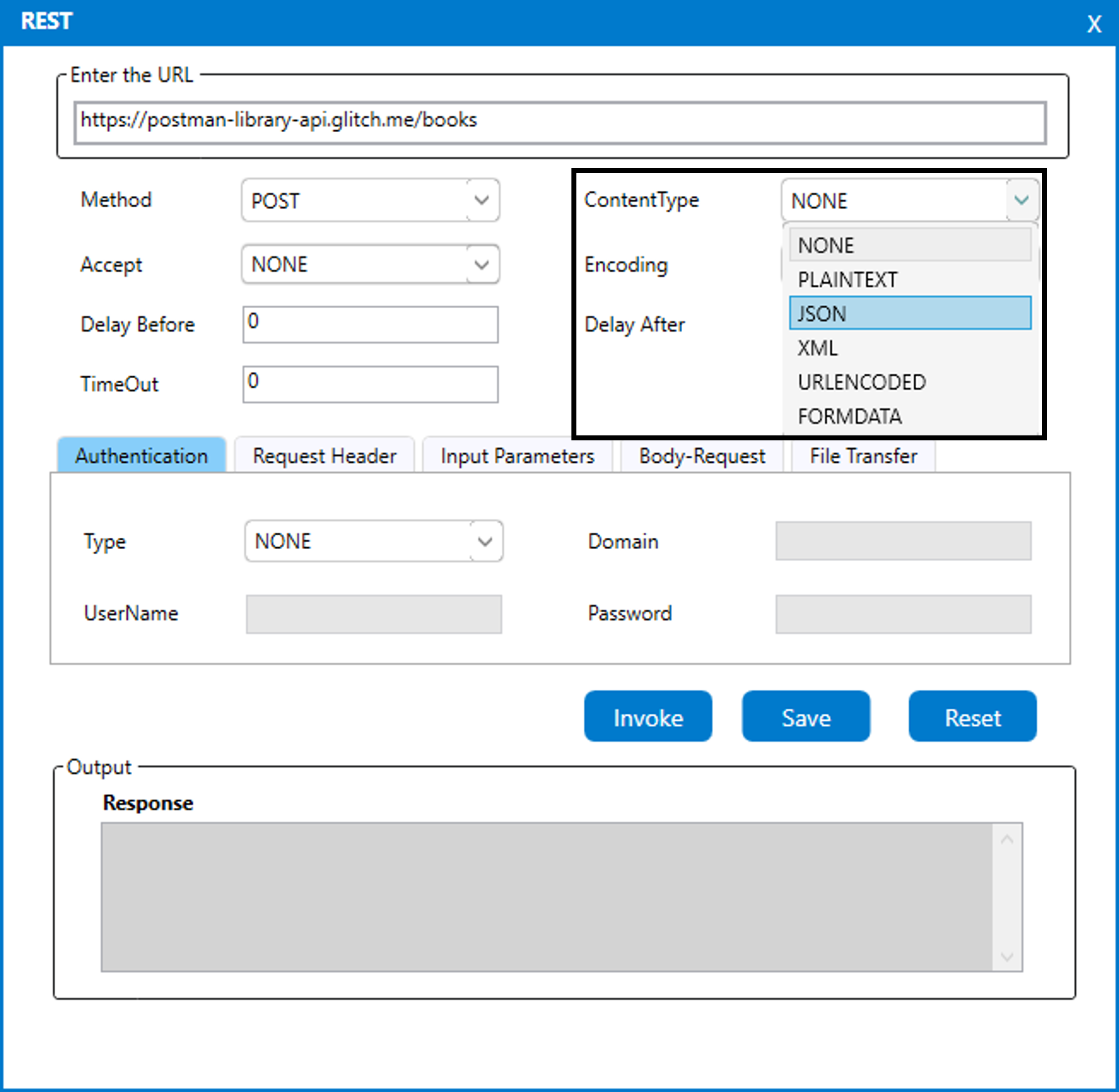
5. Choose the method as POST as we are sending the book details.
6. Choose the content type as “JSON”.
a. Since the body request is sent in “Json” format, we are opting the
value as “Json”. (Refer the below image)
7. Moving to the “Body Request” and provide the value as below,
{“title”: “Dune”, “author”: “Roger Zelazny”, “genre”: “fiction”,
“yearPublished”: "1965"}. Refer the below image.
8. Click on the Save option to export the parameters to the activity.
9. Navigating to the “Text” property in the output section to declare a variable
to view the output.
i. There are two methods to declare a variable.
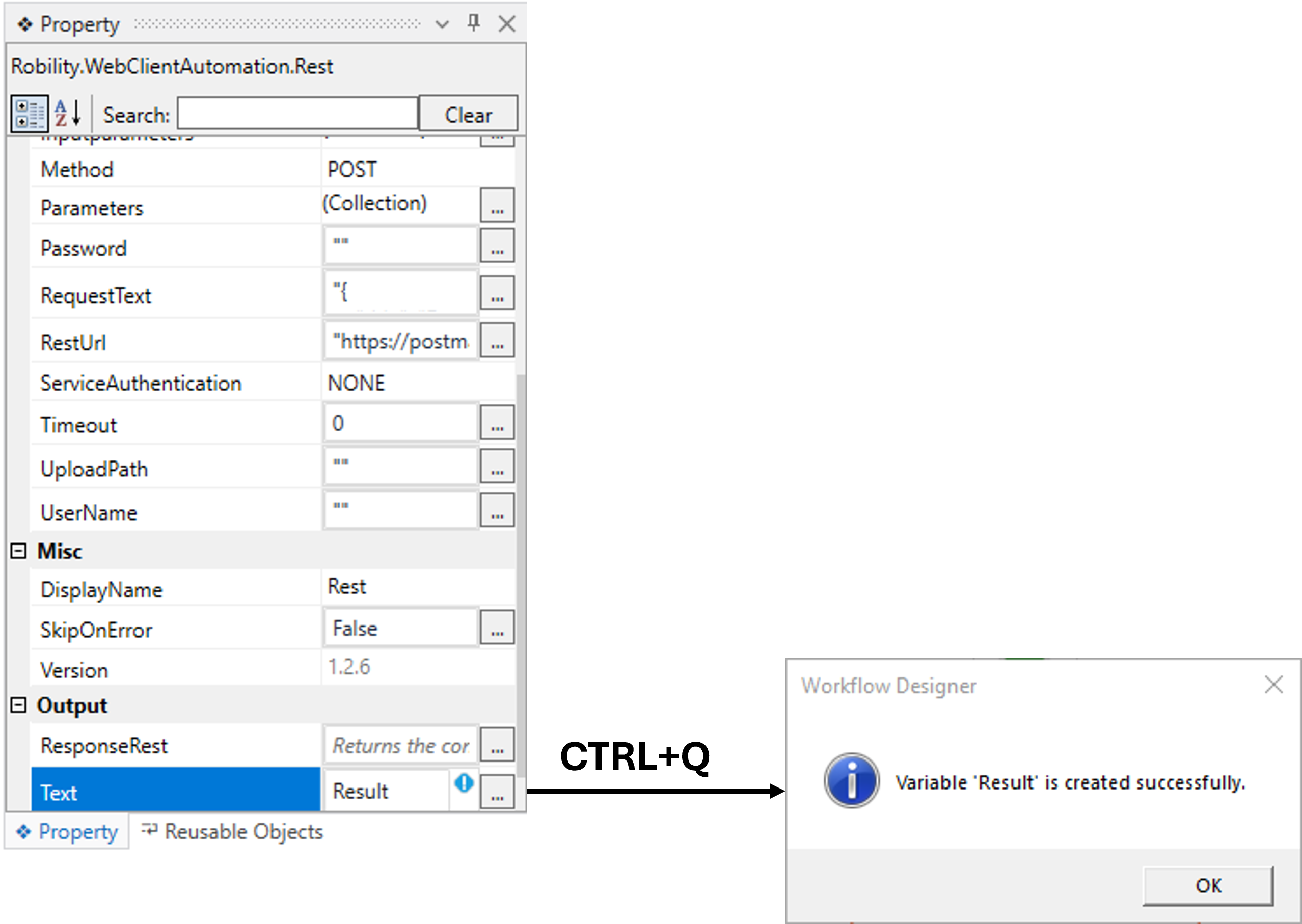
ii. Method 1: Double-click on the variable parameter in the “Output” section
and enter a name that helps you easily identify it in the flow. Here, I’m
using the name “Result” and using the shortcut key “Ctrl+Q” to create
the variable. (Refer the below image)
ii. Method 2: Click on the variable pane, enter your preferred name
(here, I’m using “Result”), and choose the data type as “String”
since the output value accepts the string data type.
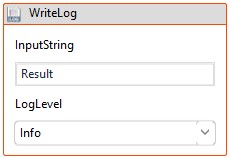
10. Add Write log activity from the “Notification” feature to view the output.
a. Here, enter the input string “Result."
b. Choose the log level as “Info”. (Refer the below image)
The bot will execute the activity and adds the provided book details
in the open-source library and returns the output as “OK”.